BRUCE L. GARY
b r u c e @ b r u c e g a r y . n e t
BRUCE L. GARY
b r u c e @ b r u c e g a r y . n e t
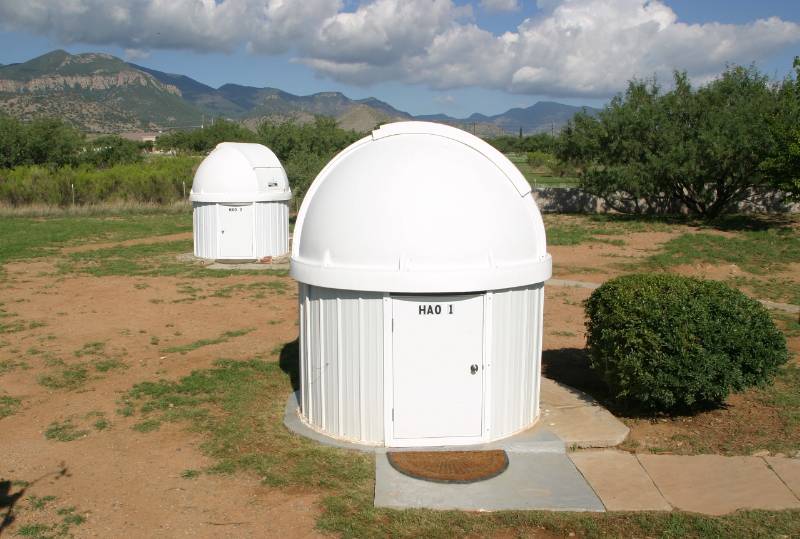
I was born in Ann Arbor, MI in 1939. After receiving a B. S. degree in Astronomy from the University of Michigan in 1961 I joined the U. S. Naval Research Laboratory's Radio Astronomy Branch (Washington, D.C.) and conducted studies of Jupiter. In 1963 I joined Caltech's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and for two years conducted microwave investigations of the moon. I worked briefly at Cornell University's Arecibo Ionospheric Observatory, in Puerto Rico. After returning to JPL's Space Sciences Division, I resumed planetary radio astronomy investigations of the moon and planets. During the remaining 33 years of my employment by Caltech, and assignment to JPL, my career underwent transitions from radio astronomy to boundary layer meteorology, then aviation safety, and finally atmospheric science of the stratosphere (with contributions to understanding the "ozone hole"). I retired from JPL in 1998, continued to work part-time for two years, then transitioned to a consulting arrangement that lasted 10 years. Additional consulting included Rockwell International (2 years), Dryden Flight Research Center (2 years), Caltech (2 years), Vanderbilt University (3 years) and Planetary Science Institute (Tucson, 1 year). With my private observatory in Hereford, AZ (pictured below) I became one of the first amateurs to observe exoplanet transits, and created the Amateur Exoplanet Archive (AXA) to accept and preserve transit observations by amateurs throughout the world (with ~640 transit entries). I continue to initiate and coordinate international teams of amateur astronomers for specific observations that support professional astronomy goals.
WORK EXPERIENCE
Planetary Radio Astronomy
From 1964 to 1972 I used radio telescopes throughout the world to construct radiometric maps of the moon at a variety of wavelengths and lunar phases. This work remains unsurpassed in quality and comprehensiveness to this day. Analysis of these maps showed that the thermophysical and electrical properties of the uppermost few centimeters of the lunar regolith are very similar over the entire near-side of the moon (with the one exception of greater ilmenite content in Mare Tranquilitatis). These results still provide the strongest argument for generalizing Apollo in situ findings.
In 1968 I accepted leadership of JPL's Radio Astronomy Group. I
wrote the software for controlling the 18-foot radio telescope at
Table Mountain Radio Observatory, performed pointing and antenna
property calibrations and assisted in development of a 36 GHz
two-element radio interferometer at TMO. One fateful day a
lightning strike of the antenna destroyed the computer and other
equipment that was needed for a long-planned monitoring program of
Venus, and by coincidence this signaled a shift in my interests
toward the use of portable ground-based systems for studying the
atmosphere.
Ground-Based Atmospheric Science (Boundary Layer)
In 1975 I joined JPL's Observational Systems Division and began applying radio astronomy remote sensing techniques to the study of atmospheric science problems. This transition away from radio astronomy led to principal investigator leadership for 41 field experiments using ground-based and airborne microwave remote sensor systems.
I supervised the development of ground-based instruments for use in the study of spatial and temporal properties of line-of-sight contents of atmospheric water vapor and cloud liquid water. Ground-based passive microwave systems were also developed for obtaining air temperature profiles. I pioneered in developing calibration techniques (including "tip curves") for water vapor radiometers as well as in the optimum use of combined mulit-frequency / multi-angle temperature profilers. These radiometer systems were used in a variety of studies, including pollution dispersion (mixing layer depth), stratus cloud formation and evolution (in collaboration with UCLA), demonstration of aviation icing hazard warnings near airports (Buffalo, NY), and numerous performance demonstrations that used radiosondes for validation.
Airborne Atmospheric Science (Microwave Temperature
Profiler)
I led the development and flight of the first airborne Microwave Temperature Profiler, MTP, in support of a 1978 study of clear air turbulence, CAT. Additional CAT studies were conducted using an improved temperature profiler installed in NASA's C-141 aircraft (Kuiper Airborne Observatory). An instrument with further improvements was installed in NASA's ER-2 aircraft and was used in the 1987 Stratospheric-Tropospheric Exchange Project, STEP. Six months later, the ER-2 Microwave Temperature Profiler was one of 25 instruments participating in the first NASA-coordinated international airborne investigation of stratospheric ozone depletion, the Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment, AAOE (Punta Arenas, Chile, 1987). The MTP instrument, in addition to providing mesoscale meteorology context for in situ measurements during this mission, also discovered that Antarctic mountain waves extend above the tropopause and throughout the region of ozone destruction, and provide a mechanism to enhance "polar stratospheric cloud" (PSC) formation, which is a crucial step in the process for the destruction of stratospheric ozone.
The same MTP was used during the 1989 Airborne Arctic Science Experiment, AASE I, based in Norway, during which I discovered that air parcel trajectories exhibit vertical "wrinkles" and therefore air parcels experience fluctuations in temperature. This discovery has implications for the understanding of PSC formation and evolution. During AASE II (Norway, Alaska, Maine 1991/92), MTP instruments were flown aboard both participating NASA aircraft, the DC-8 and an ER-2. The MTP flew on 49 ER-2 flights during the Airborne Southern Hemisphere Ozone Experiment/Measurements for Assessing the Effects of Stratospheric Aircraft, ASHOE/MAESA, based in New Zealand and Hawaii, throughout 1994, which led to studies of tracer filament temperature signature anomalies. The MTP also flew during the ER-2 Stratospheric Tracers of Atmospheric Transport, STRAT flights of 1995 and 1996, which were based in California and Hawaii. The DC-8 MTP flew during the 1995 and 1996 Tropical Ozone Transport Experiment/Vortex Ozone Transport Experiment, TOTE/VOTE, based in Hawaii, Alaska, Iceland and California. These flights have provided intriguing new information on meridional circulation.
An improved DC-8 MTP flew during the 1996 Subsonic Aircraft Contrail and Cloud Effects Study, SUCCESS, flights based in Kansas. These data were used to derive the first-ever 2-D isentrope topography for a mountain wave event over Colorado, allowing for quantification of cooling and heating histories of air parcels associated with lee wave clouds. During 1997 the ER-2 MTP participated in each of the 3 Photochemistry of Ozone Loss in the Arctic Region in Summer, POLARIS, campaigns, based in Fairbanks, AK. Isentrope surfaces were found to be surprisingly smooth for this season and latitude, which inspired a comprehensive study showing that the amplitude of mesoscale vertical motions in the stratosphere can be predicted from four independent variables: latitude, season, altitude and underlying topography (two article links below).
The DC-8 MTP was used in the Fall of 1997 for the
SASS Ozone and Nitrogen Oxides Experiment, SONEX, based in
Ireland and Bangor, ME, for the study of atmospheric chemistry
impacts of subsonic aircraft. The ER-2 MTP was flown in an Air
Force WB-57F during the Spring of 1998 for the Water Aerosol
Mission, WAM, based in Texas. Dr. Mahoney was co-investigator
for the last two experiments. I discontinued full-time
employment from JPL on September 25, 1998, and
for two years was employed by Caltech's JPL as an "on-call"
employee for the purpose of providing occasional assistance to
Dr. Mahoney, who is now the MTP Principal Investigator. From
2000 - 2010 I was a consultant for JPL in continued support of
airborne MTP projects.
After I retired Dr. M. J. Mahoney took over as
PI, and with Richard Denning continued to develop improved MTP
models that were flown on various NASA atmospheric research
aircraft. Here's a video made shortly before M.J. died, in which
he and Richard explain how MTP works and its role in the NASA
ATTREX mission: link.

AWARDS AND RELATED HONORS
BOOK PUBLICATIONS
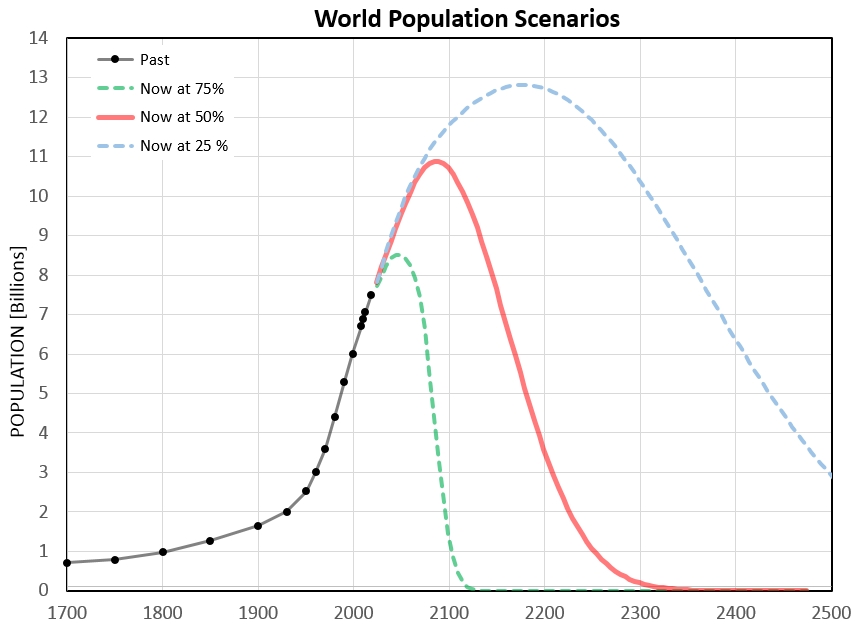 The case for connecting fossil fuel burning with global warming is as strong as the case for connecting smoking with lung cancer. Each belongs to a category of small present reward versus the risk of possible far-future calamity. But why are humans like this? It has to do with the genes, which assemble us for serving their purposes. We are designed to act like unthinking robots! If the genes allowed “why thinking” some of us would begin to act in ways that serve individual welfare, at the expense of serving the genes with their apparent goal of genetic immortality. It’s because people are born with blinders that “reason” has no sway in averting future catastrophe. This underlies my feeling of futility as I glean more insight into the coming darkness. This graph of possible scenarios for future world population is based on the assumption that the entirety of humanity can be considered to be a finite sequence, thus allowing use of sampling theory to estimate the end of the sequence. |
2006: Shankland, P. D., E. J. Rivera, G. Laughlin, D. L. Blank, A. Price, B. Gary, R. Bissinger, F. Ringwald, G. White, G. Henry, P. McGee, A. S. Wolf, B. Carter, S. Lee, J. Biggs, B. Monard, "On the Search for Transits of the Planets Orbiting GL 876," Ap J, Part 1, ms65295, 2006: http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0608489
2006: Gary, B. L., "Mesoscale Temperature Fluctuations in the
Stratosphere" Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2006: http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/6/4577/2006/acp-6-4577-2006.html
2006: McCullough, P.R., Stys, J. E., Valenti, J. A., Johns-Krull, C. M., Janes, K. A., Heasley, J. N., Bye, B. A., Dodd, C., Fleming, S. W., Pinnick, A., Bissinger, R., Gary, B. L., Howell, P. J., Vanmunster, T., "A Transiting Planet of a Sun-like Star", Astrophys. J., 648, 2, 1228-1238, September, 2006.
2006: Gary, Bruce L. and David Healy, "Image Subtraction
Procedure for Observing Faint Asteroids," The Minor Planet
Bulletin, 33, 1, January-March 2006: link
2005: Price, A, and 16 others, "Planetary Transits of the Trans-Atlantic Exoplanet Survey Candidate TrES-1b," J. Amer. Assoc. Var. Star Obs., 34, 17, 2005.
2005: Gary, Bruce L., The Making of a Misanthrope: Book 1,
Hereford, AZ: BLG Publishing, August, 2005.
2004: Pan, L. L., W. J. Randel, B. L. Gary, M. J. Mahoney and E.
J. Hintsa, "Definitions and Sharpness of the Extratropical
Tropopause: A Trace Gas Perspective, J. Geophys. Review, 109,
D23103, 2004.
2004: Price, A. and 32 others, "A New Cataclysmic Variable in
Hercules," PASP, December 2004.
2004: Price, A. T. Vanmunster, D. Starkey, D. Boyd, R. Zissell,
B. Gary, K. Graham, W. Macdonald II, B. Aquino, D. West, J.
Blackwell, G. Walker, M. Simonsen, A. Henden, M. R. Templeton, J.
A. Mattei, "Flickering and Periodic Activity in the 2004 Outburst
of BZ UMa," Information Bulletin on Variable Stars (IBVS),
# 5526, 2004: link
2004: Gary, B. L., "CCD Photometry of Asteroid 12753 Povenmire,"
Minor Planet Bulletin, 31, #3, 2004: link
2004: Gary, B. L., Genetic Enslavement: A Call to Arms for
Individual Liberation, Hereford, AZ: BLG Publishing: link
Jensen, E. J., O. B. Toon, A. Tabazadeh, G. W. Sachse, B. E. Anderson, K. R. Chan, C. W. Twohy, B. Gandrud, S. M. Aulenbach, A. Heymsfield, J. Hallett, B. Gary, "Ice Nucleation Processes in Upper Tropospheric Wave-Clouds Observed During SUCCESS," Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, 1363-1366, May 1, 1998.
Dean-Day, J., K. R. Chan, S. W. Bowen, T. P. Bui, B. L. Gary, M. J. Mahoney, "Dynamics of Rocky-Mountain Lee Waves Observed During SUCCESS," Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, 1351-1354, May 1, 1998.
Burris, J., W. Heaps, B. Gary, W. Hoegy, L. Lait, T. McGee, M. Gross, U. Singh, "Lidar Temperature Measurements During the TOTE/VOTE Mission," J. Geophys. Res., 103, 3505-3510, 1998.
Hintsa, E. J., K. A. Boering, E. M. Weinstock, J. G. Anderson, B. L. Gary, L. Pfister, B. C. Daube, S. C. Wofsy, M. Lowenstein, J. R. Podolske, J. J. Margitan, T. P. Bui, "Troposphere-to-Stratosphere Transport in the Lowermost Stratosphere from Measurements of H2O, CO2, N2O and O3," Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, 2655-2658, July 15, 1998.
Tabazadeh, A., O. B. Toon, B. L. Gary, J. T. Bacmeister, M. R. Schoeberl, "Observational Constraints on the Formation of Type Ia Polar Stratospheric Clouds," Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 2109-2112, Aug. 1, 1996.
Bacmeister, Julio T., Stephen D. Eckermann, Paul A. Newman, Leslie Lait, K. Roland Chan, Max Lowenstein, Michael H. Proffitt, Bruce L. Gary, "Stratospheric Horizontal Wavenumber Spectra of Winds, Potential Temperature, and Atmospheric Tracers Observed by High-Altitude Aircraft," J. Geophys. Res., 101, D5, 9441-9470, Apr. 27, 1996.
Murphy, D. M., B. L. Gary, "Mesoscale Temperature Fluctuations and Polar Stratospheric Clouds," J. Atmos. Sci., 52, 1753-1760, May 15, 1995.
Weinheimer, A. J., J. G. Walega, B. A. Ridley, B. L. Gary, D. R. Blake, N. J. Blake, F. S. Rowland, G. W. Sachse, B. E. Anderson, J. E. Collins, "Meridional Distribution of NOx, NOy, and Other Species in the Lower Stratosphere and Upper Troposphere During AASE II," Geophys. Res. Lett., 21, 2583-2586, Nov. 15, 1994.
Bacmeister, J. T., P. A. Newman, B. L. Gary, K. R. Chan, "An Algorithm for Forecasting Wave-Related Turbulence in the Stratosphere," Weather and Forecasting, 9, 2, June 1994.
Pueschel, R. F., G. V. Ferry, S. Verma, S. D. Howard, B. Gary, J. M. Livingston, P. Newman, J. E. Dye, D. Baumgardner, "Northern Polar Vortex Aerosol Variability," submitted to Geophys. Res. Letters, June 1993.
Chan, K. R., L. Pfister, T. P. Bui, S. W. Bowen, J. Dean-Day, B. L. Gary, D. W. Fahey, K. K. Kelly, C. R. Webster, and R. D. May, "A Case Study of the Mountain Lee Wave Event of January 6, 1992," Geophys. Res. Lett, 20, 2551-2554, Nov. 19, 1993.
Toon, O. B., E. V. Browell, B. Gary, R. Pueschel, P. Russell, M. Schoeberl, G. C. Toon, F. Valero, H. Selkirk, J. Jordan, "Heterogeneous Reaction Probabilities, Solubilities, and Physical State of Cold Sulfuric Acid Aerosols," Science, August 27, 1993.
Pfister, L., K. R. Chan, T. P. Bui, S. Bowen, M.
Legg, B. Gary, K. Kelly, M. Proffitt, W. Starr, "Gravity Waves
Generated by a Tropical Cyclone During the STEP Tropical Field
Program: A Case Study," J. Geophys. Res., 98, D5,
8611-8638, May 20, 1993.
Russell, P. B., O. B. Toon, E. V. Browell, G. C.
Toon, B. Gary, M. Schoeberl, F. P. J. Valero, R. Pueschel,
"Combined Use of Microwave and Optical Measurements on the NASA
DC-8 to Determine Aerosol and Gas Properties Related to Ozone
Depletion," Proceedings of IEEE Topical Symposium on Earth and
Atmosphsere Sensing, 1993 March 22-25, ISBN 0-7803-0969-3.
Dye, J. E., B. W. Gandrud, S. R. Kawa, K. K. Kelly, M. Lowenstein, G. V. Ferry, K. R. Chan, and B. L. Gary, "Particle Size Distributions in Arctic Polar Stratospheric Clouds: Growth and Nucleation of Sulfuric Acid Droplets and Implications for Cloud Formation," J. Geophys. Res., 97, 8015-8034, May 30, 1992.
Gary, B. L. and S. J. Keihm, "Microwave Sounding Units and Global Warming," Science, 251, 316, 1991 Jan 18, link.
Bacmeister, J. T., M. R. Schoeberl, L. R. Lait, P. A. Newman and B. Gary, "Small-Scale Waves Encountered During AASE," Geophys. Res. Lett., 17, 349-352, 1990.
Bacmeister, J. T. and B. Gary, "ER-2 Mountain Wave Encounter Over Antarctica: Evidence for Blocking," Geophys. Res. Lett., 17, 81-84, 1990.
Gandrud, R. W., J. E. Dye, D. Baumgardner, G. V. Ferry, M. Lowenstein, K. R. Chan, L. Sanford, B. Gary and K. Kelly, "The January 30, 1989 Arctic Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) Event: Evidence for a Mechanism of Dehydration," Geophys. Res. Lett., 17, 457-460, 1990.
Lait, R. L., M. R. Schoeberl, P. A. Newman, M. H. Proffitt, M. Lowenstein, J. R. Podolske, S. E. Strahan, K. R. Chan, B. Gary, J.J. Margitan, E. Browell, M. P. McCormick and A. Torres, "Reconstruction of O3 and N2O Fields from ER-2, DC-8, and Balloon Observations, Geophys. Res. Lett., 17, 521-524, 1990.
Gary, B. L, "Observational Results Using the Microwave Temperature Profiler During the Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment," J. Geophys. Res., 94, 11,223-11,231, 1989.
Denning, R. F., S. L. Guidero, G. S. Parks and B. L. Gary, "Instrument Description of the Airborne Microwave Temperature Profiler," J. Geophys. Res., 94, 16,757-16,765, 1989.
Hartmann, D. L., K. R. Chan, B. L. Gary, M. R. Schoeberl, P. A. Newman, R. L. Martin, M. Lowenstein, J. R. Podolske and S. E. Strahan, "Potential Vorticity and Mixing in the South Polar Vortex During Spring," J. Geophys. Res., 94, 11,625-11,640, 1989.
Proffitt, M. H., K. K. Kelly, J. A. Powell and B. L. Gary, "Evidence for Diabatic Cooling and Poleward Transport Within and Around the 1987 Antarctic Ozone Hole," J. Geophys. Res., 94, D14, 16,797-16,813, 1989.
Proffitt, M. H., J. A. Powell, A. F. Tuck, D. W. Fahey, K. K. Kelly, A. J. Krueger, M. R. Schoeberl, B. L. Gary, J. J. Margitan, K. R. Chan, M. Lowenstein and J. R. Podolske, "A Chemical Definition of the Boundary of the Antarctic Ozone Hole," J. Geophys. Res., 94, D9, 11,437-11,448, 1989.
Wilson, J. C., M. Lowenstein, D. W. Fahey, B. Gary, S. D. Smith, K. K. Kelly, G. V. Ferry and K. R. Chan, "Observations of Condensation Nuclei in the Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment: Implications for New Particle Formation and Polar Stratospheric Cloud Formation," J. Geophys. Res., 94, D14, 16,437-16,448, 1989.
Schoeberl, M. R., L. R. Lait, P. A. Newman, R. L. Martin, M. H. Proffitt, D. L. Hartmann, M. Lowenstein, J. Podolske, S. E. Strahan, J. Anderson, K. R. Chan and B. Gary, "Reconstruction of the Constituent Distribution and Trends in the Antarctic Polar Vortex From ER-2 Flight Observations," J. Geophys. Res., 94, D14, 16,815-16,845, 1989.
Conel, James E., Robert O. Green, Veronique Carrere, Jack S. Margolis, Ronald E. Alley, Gregg Vane, Carol L. Bruegge, and Bruce L. Gary, "Atmospheric Water Mapping with the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS)," Conference Procedings, JPL Publication 87-38, 1987.
Treuhaft, R. N., C. D. Edwards, B. L. Gary, G. E. Lanyi, S. E. Robinson, "Temporal Water Vapor Fluctuations for Phase-Delay Interferometric Geodesy," EOS, 67, 914, 1986.
Gary, B. L., S. J. Keihm and M. A. Janssen, "Optimum Strategies and Performance for the Remote Sensing of Path-Delay Using Ground-Based Microwave Radiometers," IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing, GE-23, 479-484, 1985.
Gary, B. L., "Clear Air Turbulence Avoidance Using an Airborne Microwave Radiometer," AIAA Pap., AIAA-84-0273, 1984.
Gary, B. L., "An Airborne Remote Sensor for the Avoidance of Clear Air Turbulence," AIAA Pap., AIAA-81-0297, 1981.
Janssen, M. A., B. L. Gary, S. Gulkis, E. T. Olsen, F. S. Soltis and N. I. Yamane, "The Table Mountain 8-mm Wavelength Interferometer," IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagation, AP-27, 759-763, 1979.
Keihm, S. J. and B. L. Gary, "Comparison of Theoretical and Observed 3.55 cm Wavelength Brightness Temperature Maps of the Full Moon," Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 10th, 2311-2319, 1979.
Gary, B. L. and S. J. Keihm, "Interpretation of Ground-Based Microwave Measurements of the Moon Using a Detailed Regolith Properties Model," Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 9th, 2885-2900, 1978.
Gary, B. L., "Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus Disk Temperature Measurements at 2.07 and 3.56 cm," Atronom. J., 79, 318-320, 1974.
Gulkis, S., B. Gary, M. Klein and C. Stelzried, "Observations of Jupiter at 13-cm Wavelength During 1969 and 1971," Icarus, 18, 181-191, 1973.
Gary, B. L., E. T. Olsen and P. W. Rosenkranz, "Radio Observations of Cygnus X-3 and the Surrounding Region," Nature, 95, 128-130, 1972.
Gulkis, S. and B. Gary, "Circular Polarization and Total Flux Measurements of Jupiter at 13.1 cm Wavelength," Astronom. J., 76, 12-16, 1971 (link).
Gary, B. and S. Gulkis, "New Circular Polarization Measurements of Jupiter's Decimeter Radiation," Astronom. J., 158, L193-195, 1969 (link).
Gary, B., "Results of a Radiometric Moon-Mapping Investigation at 3 Millimeters Wavelength," Astrophys. J., 147, 245-254, 1967 (link).
Gary, B., "Mercury's Microwave Phase Effect," Astronom. J., 149, L141-145., 1967 (link).
Gary, B., J. Stacey and F. D. Drake, "Radiometric Mapping of the Moon at 3 Millimeters Wavelength," Astrophys. J., Supp. 108, XII, 239-262, 1965 (link).
Gary, B., "An Investigation of Jupiter's 1400 Mc/sec Radiation," Astronom. J., 68, 568-572, 1963. (using Bayesian Estimation Theory without realizing it, link)
Miller, A. C. and B. L. Gary, "Measurements of
the Decimeter Radiation from Jupiter," Astronom. J., 67,
727-731, 1962 (link).
________________________________________________________________
This site opened: 1998.08.25. Last Update: 2025.07.02